When the European Union passed the GDPR back in 2018, it changed how the world thought about data privacy. Now, the EU is doing the same thing—but this time with artificial intelligence.
Say hello to the EU AI Act: the world’s first comprehensive law regulating AI.
Just as laws around cars, electricity, or medicine were needed to keep people safe as those technologies became widespread, the EU AI Act steps in to guide how artificial intelligence is used—especially in places where it can impact our lives in powerful, personal ways.
But what exactly is the EU AI Act? Whom does it affect? What’s in it for me? And is this going to slow down progress or make our world safer?
Let’s break it down.
What Is the EU AI Act?
Think of the EU AI Act as the “seatbelt law” of artificial intelligence. It’s not banning cars (or AI), but it is making sure they have brakes, seatbelts, and headlights before they’re allowed on the road.
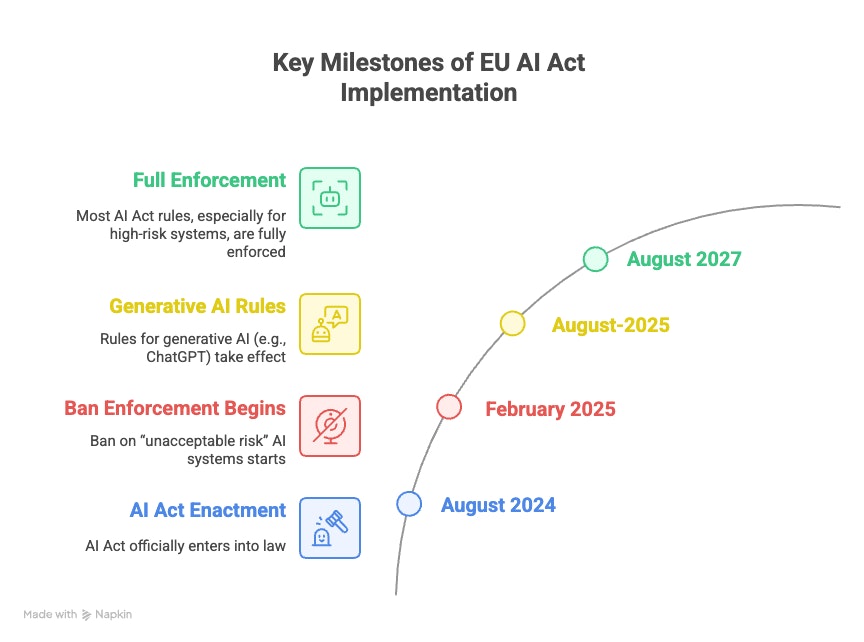
The EU AI Act became law in August 2024 after over three years of negotiations and debate. The goal? To make sure AI is used safely, transparently, and fairly across the 27 countries in the EU—and possibly influence AI regulation globally.
This matters because AI isn’t some abstract futuristic idea anymore. It’s already here, powering healthcare diagnoses, self-driving cars, chatbots, online recommendations, and even decisions about who gets a loan or a job interview.
The stakes are enormous. And that’s exactly why the EU decided it was time to draw a line between helpful AI and harmful AI.
At the Heart of It: A Risk-Based Approach
The EU AI Act doesn’t treat all AI the same. Not all tech is equally dangerous.
Nobody’s worried about the AI in your Netflix recommendations. But what about the AI that tracks people in crowds? Or decides whether you get a mortgage or a bail?
To make sense of this wide sweep, the Act classifies AI systems into four risk categories:
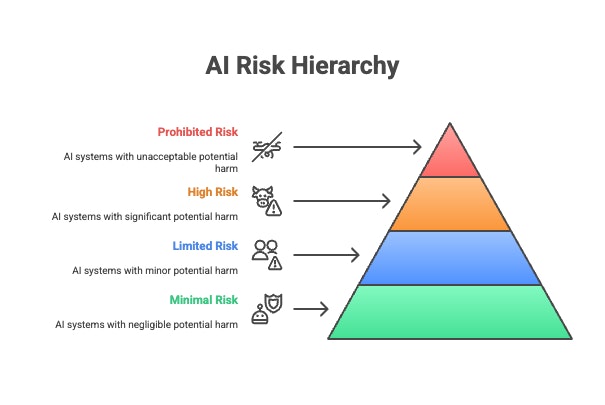
1. Minimal Risk
These are everyday applications, like AI in spam filters or your favorite photo-editing app. They’re so low-risk that the law doesn’t impose any new rules here.
✅ No worries, no rules.
2. Limited Risk
These tools include things like chatbots and AI-generated media. You just need to be transparent that AI is involved.
For example, websites using AI to answer your questions should tell you it’s AI,so you’re not misled into thinking it’s a real person.
🧾 Requirement: Disclosure and basic transparency.
3. High Risk
Here’s where things get serious. High-risk AI includes systems that make or support decisions in sensitive areas:
- Education (like grading algorithms)
- Employment (like AI hiring tools)
- Law enforcement (like facial recognition).
- Healthcare (like AI diagnostics).
If you’re using AI for things that can impact rights, safety, or freedoms, you’ll need to follow clear rules:
✅ Use high-quality data.
✅ Keep detailed records.
✅ Built-in oversight
✅ Allow human intervention.
In other words, you need to prove your AI system is safe, fair, and accountable.
📝 These systems must be registered in an EU database and undergo strict assessments.
4. Unacceptable Risk (Banned AI)
Some AI systems are considered too dangerous to be allowed at all. These include:
- Social scoring systems like China’s social credit model
- Real-time, mass facial recognition in public areas
- AI that manipulates people’s behavior, especially kids (e.g., toys that encourage dangerous actions).
🚫 These systems are outright banned.
Why This Matters for You
Chances are, you’re already interacting with AI every day whether you know it or not. The EU AI Act gives you some important rights:
- You have the right to be told if content was generated or altered by AI (think deepfakes).
- You can submit complaints if you think a high-risk AI made an unfair or wrong decision about you.
- You get more protection from being surveilled or manipulated without your consent.
In short, the law aims to make AI more understandable, more accountable, and less creepy.
And if you’re not in the EU? This could still affect you.
Just like the GDPR changed global practices around data privacy because companies needed to comply in order to serve European customers, many businesses worldwide will end up following the AI Act’s standards just to stay in the EU market.
For Businesses: Get Ready to Comply or Pay the Price
For corporate leaders and startups, this law is a wake-up call. If you build, sell, or deploy AI products in Europe, you now have a checklist of compliance steps.
And yes—it’s serious.
Break the rules, and you could face fines of up to 7% of global annual revenue. That’s not small change, especially for tech giants.
But it’s not all bad news; there’s support built in. Companies (especially smaller ones) will gain access to “AI regulatory sandboxes” where they can develop and test their products in a safe, supervised environment.
This allows innovation to happen without crossing legal (or ethical) lines. Think of it like giving learners a protected racetrack before letting them drive on the highway.
Timeline: What’s Happening When?
Case Study: ChatGPT and Generative AI
Let’s take a closer look at generative AI, tools like ChatGPT, Midjourney, or AI music generators.
Under the Act, these tools aren’t banned, but they do come with conditions:
- Platforms must label AI-generated content clearly.
- Developers must stop their models from producing illegal content.
- Companies must disclose the copyrighted material used to train AI models.
For instance, if a song is generated entirely by AI, it should say so. If an image looks like a photo but was AI-generated, there should be a label.
This not only protects creators and users but also helps preserve truth in an age of deepfakes and AI “hallucinations.”
By requiring these disclosures, the EU hopes to build trust in AI systems and perhaps curb the spread of misinformation.
The Big Question: Does This Kill Innovation?
This is where opinions split.
Supporters say the EU AI Act is a breakthrough. It makes sure that humans, not tech, stay in charge. It protects our rights and keeps us safe. And by setting global standards, it can prevent a digital version of the “Wild West.”
Critics, however, worry about bureaucracy, delays, and costs, especially for startups and small businesses.
A 2023 study by startup advocacy group Allied for Startups estimated that compliance costs for AI businesses could consume up to 2.7% of annual revenues. That’s a big deal if you’re trying to build the next AI unicorn on a shoestring budget.
As Dr. David, a privacy educator, puts it in his recent video, “AI’s power is immense.” But with that power comes real risks. “Would you want an AI slipping up during your surgery or mislabeling a criminal in court?”
Final Thoughts: The First Step in a Long Road
The EU AI Act is the beginning of a new era, not just for Europe, but for the world.
The wild west of AI experimentation we live in now might not last, and we will soon see more guardrails put in place that will shape how we interact with AI.
Whether it grows into a global blueprint for responsible AI, or turns into a bureaucratic speed bump depends on how it’s implemented and adapted over time.
For now, what’s clear is this: AI is too powerful to leave unregulated and too promising to ignore.
Sources :
- https://www.europarl.europa.eu/topics/en/article/20230601STO93804/eu-ai-act-first-regulation-on-artificial-intelligence#what-parliament-wanted-in-ai-legislation-2
- https://artificialintelligenceact.eu/ai-act-explorer/
- https://www.europarl.europa.eu/topics/en/article/20230601STO93804/eu-ai-act-first-regulation-on-artificial-intelligence#encouraging-ai-innovation-and-startups-in-europe-4
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s_rxOnCt3HQ&ab_channel=EUMadeSimple
- https://www.europarl.europa.eu/topics/en/article/20230601STO93804/eu-ai-act-first-regulation-on-artificial-intelligence#ai-regulation-in-europe-the-first-comprehensive-framework-4
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wDW3XMHrA4M&ab_channel=Dr.David%2CPrivacyEducator





