So What is AI??? A new digital species? Your resident digital assistant? Is it just a buzzword for companies to increase their shareholder value? A groundbreaking breakthrough or an innovation that could solve the most vital human problems and perhaps pose existential dangers.
There has been a lot of talk about AI, but what is this digital sorcery, and should we be excited or afraid?
But it’s not that complicated after all—it’s no magic, but multimillion-dollar science with huge data and computing power you never imagined.
What is artificial intelligence?
AI, or artificial intelligence, is the development of computer systems able to carry out tasks that are normally associated with human intelligence only. It is the action of computing human thought, which includes a wide variety of capabilities and complexity.
AI technologies are used to replicate human cognitive functions such as learning and problem-solving. We must, however, realize that human intelligence is not purely cognitive. While we often benchmark AI against human intelligence, this can be both deceptive and degrading to the very point of creating it to begin with.
Human intelligence can bend and stretch in amazing ways. By doing these, we can make decisions without needing 100% of the information, use our imagination, and understand things in context. On the other end of the spectrum, AI has everything to do with data and pattern recognition. It can uncover insights and connections in hitherto incomprehensible datasets that would take mankind years to discover, yet it can also make embarrassing conclusions if not explicitly taught about the information you deem so simple.
As you can see, the difference between AI bots and most of what passes for AI seems to be huge.
Now, there are three primary categories into which we can divide them:
Superintelligent AI: This is the level above general AI; it refers to any artificial intelligence that significantly exceeds human capabilities in almost every field. Status: The source of futurists’ utopian dreams and dystopian nightmares—it’s strictly hypothetical.
Narrow AI (or Weak AI): This is the type of AI we interact with on a daily basis. The reference “narrow” means that it’s engineered to do specific types of work very well. Narrow AI is more speweakized and functions like a very sharp tool. It does a very particular kind of job very well, but becomes very ambitious when asked to do anything else. In other words, your chess AI (great as it is at winning that game) won’t be able to help you order pizza.
General AI (or Strong AI): Popular conceptions of this form of AI include machines which can operate and behave in such a way that their consciousness mirrors those of men. And it would be capable of executing virtually every cognitive deed a person could. Today: Still not there, and it’s hard to fathom getting there in the future.
How does AI work? The Basics
Under the AI umbrella, we have multiple technologies, ie machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing. AI, at its heart, is data-driven pattern recognition.
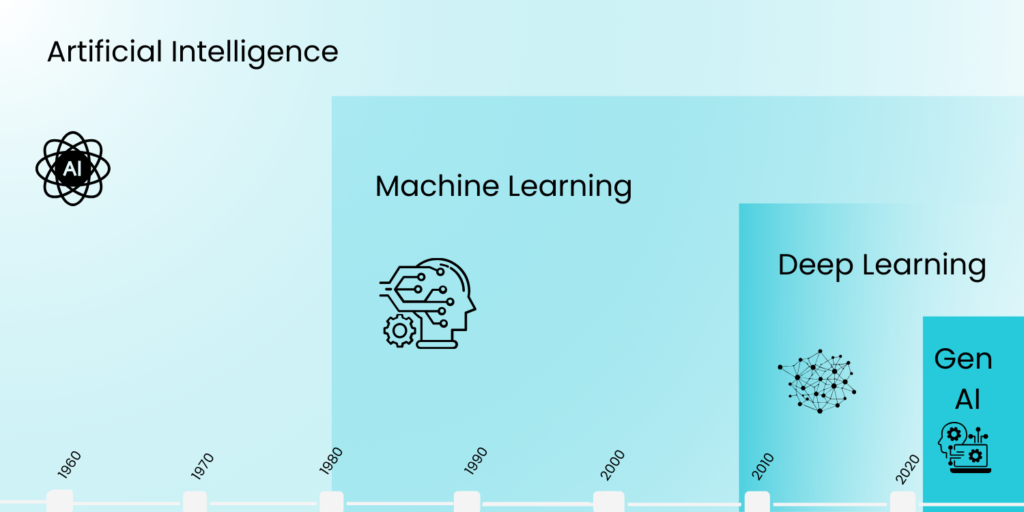
The evolution of AI systems
AI systems function by:
- Ingesting large amounts of data
- Analyzing the data for correlations and patterns
- Using these patterns to make predictions or decisions
At a fundamental level, AI is still a computer that has the ability to automatically connect dots that humans might never have seen. This is one of the basic reasons why AI achieves its power and versatility.
It is like trying to learn a new language. At first, they all sound like Jibberish. However, eventually you realise there are some patterns to it—some sounds are more likely to occur at the end of a question, or words tend to follow each other. AI is similar to that, but it operates at a much faster speed and on a larger scale.
An explanation of the process AI goes through:
- Input of data: AI systems take in huge amounts of data. This can be any kind of data, not limited to images, text, numbers or recordings of birds singing.
- Finding Similarities: this data is split up and the AI hunts for similarities and differences within it It might start with something as simple as every thousand or so cat pictures; there seems to be some round thing with pointy bits at the top (ears!).
- Creating Rules: The AI will process these patterns and establish rules. If it has pointy ears, whiskers, and a tail, then it’s likely a cat.
- Applying Knowledge: When the AI is fed new data, it uses these rules to decide or predict.
- Learning and improving: If the AI makes a mistake, it can change its operating rules, becoming more accurate over time.
AI is able to do this due to its ability to recognize patterns. Some examples include:
- Recognize faces in photos
- Generalize preferences of movies based on historical views
- How do detect credit card fraud?
- Preempt maintenance needs before machinery shuts down
The magic of AI is it’s ability to identify patterns in data at a record speed and then figures out what is really going on.
AI can solve problems that would be impractical or time-consuming for a human to do alone, in turn giving accuracy and other benefits not achievable by the human brain, used at levels it ought to be. It has given robotics capabilities that humans could never dream of earlier, which is breaking new ground on every front, from medical science to searching for extra terrestrial life and all about exploring space.
Artificial intelligence is not about replacing human intelligence. It’s about amplifying human intelligence.
Fei-Fei Li
From reactive to proactive AI
Generative AI, the most recent advancement in AI capabilities, has exploded since 2023. This latest addition to the AI family of things, this “new baby” in the AI family, goes beyond analysis and begins generating new content, giving birth to a new subfamily of proactive AI.
That said, generative AI is very powerful and has the ability to revolutionise many parts of consumer and business life, but it cannot and will not be the only one in the public domain. It’s crucial to remember that it’s not the only AI out there.
Many other AI applications tend to be overshadowed by the hype surrounding generative AI. Here’s some examples we are familiar with:
- Smartphone Assistants: Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa as voice assistants and questions.
- Social Media Feeds: personalized content on Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, and more.
- Email filters like spam detection and sorting (Gmail, Outlook, etc.).
- Streaming Recommendations: Content suggestions on Netflix, Spotify, and YouTube.
- Smart Home Devices: Those might include smart thermostats, lights, or security systems under the internet-of-things (IoT) umbrella (like those from Nest).
- Online Shopping: Product Suggestions on Amazon, Chat Bots in Customer Service.
- Photo Organization: Google Photos and Apple Photos for facial recognition and auto-categorization.
- Autocorrect and Predictive Text: keyboard apps that understand your writing style.
Conclusion:
As we delved into, AI is a powerful technology that is already part of our daily lives, from the smartphones in our pockets to the services we use everyday. The potential of AI to identify patterns, generalise from data and predict results is changing industries and creating avenues for future opportunities that none of us could ever foresee.
Looking Ahead:
Knowing what AI is and how it functions are only the first steps. In our follow-up post, “AI: Why does it matter and what it mean for you and me?” we will take an even deeper look into the impact of this new tech.






